I’ve previously written about How to edit AVCHD footage on Mac OSX, at the time of writing that article there weren’t many options for editing AVCHD footage on either Mac OSX or Windows operating systems. VoltaicHD is a great application that helped Mac OSX users in particular because at that time there was no way of editing AVCHD on Mac at all.
Many Mac users had purchased AVCHD cameras and were frustrated by the complete lack of software available for editing AVCHD on Mac and even Windows users had to wait quite a few months before Sony released a version of their Vegas software that supported AVCHD.
Since then though, there are quite a few options for Mac users: Final Cut Studio and Final Cut Express offered mid to high end products for the Mac platform. Also Apple’s own iMovie software had a complete revamp and amongst many new features was direct support for AVCHD based cameras, a perfect budget solution as the software was included free with any new Mac or as part of Apple’s iLife suite for about £55 / $79.
However for Windows users, despite the availability of software like Sony Vegas, many people wanted a way to edit AVCHD without having to buy editing software that cost as much (or more!) than they spent on their cameras in the first place! There was no easy way to do this on a low budget, you could find articles on the web with instructions on how to use various applications or utilities to convert the AVCHD files into various formats, but nothing simple that would allow non-technical users to edit AVCHD footage. But now there is an easy solution.
VoltaicHD for PC & Windows Movie Maker: A low budget way to edit AVCHD!
The company that produced the VoltaicHD application for Mac OSX, Shedworx, has released a Windows version of VoltaicHD that is compatible with both Windows XP and Vista. You can convert your AVCHD footage into WMV or AVI format video which can then be used with Windows Movie Maker or other video editing application for Windows.
Windows Movie Maker is a video editing package that comes with both XP and Vista, and contrary to popular belief it is actually capable of working with HD video footage, but just not with native AVCHD footage. That’s where VoltaicHD fits in, by converting the footage to WMV format you can edit the footage from your HD video camera using just Windows Movie Maker!
Tips for converting / editing AVCHD with Voltaic and Windows Movie Maker
There are a few minimum system requirements to run VoltaicHD for PC but any reasonably modern PC should be capable of processing the AVCHD files. It’s worth noting of course that HD video is very intensive to work with and requires greater resources than editing conventional standard definition video footage. On a system with the minimum hardware requirements (as detailed below) it will take about 2 minutes to convert a 10 second AVCHD clip. It is obviously recommended to have as powerful a system as you can manage but even a slightly older machine should be capable of producing results – as long as you have a little patience and perspective! On the plus side the converted video files result in uncompressed HD video which can be played back more easily than the original AVCHD files on the minimum hardware spec machine.
Minimum Hardware requirements: At least 1GB of RAM, at least a 2Ghz P4 processor or equivalent processor and as much hard disk space as possible. AVCHD footage uses about 120Mb per minute of video footage, once this footage has been processed it uses about 500Mb per minute of video, so disk space is quickly used up.
Minimum Software requirements: Either Windows XP SP2+ or Vista, Microsoft Movie Maker 2.1+ and Windows Media Player v11+.
VoltaicHD can convert AVCHD footage to either WMV or AVI formats, however WMV is the preferred format as it keeps the aspect ratio correct no matter the resolution of your source AVCHD footage. There is no loss in picture quality when converting the AVCHD footage to either WMV or AVI. However, the audio track is affected during conversion, AVCHD can use Dolby 5.1 surround sound but only Sony cameras use this, Panasonic, Canon and JVC use stereo only. Any Dolby 5.1 sound is dropped back to stereo audio as this is all that Window Movie Maker supports.
Converting files using VoltaicHD for PC
You need set up the various preferences before using VoltaicHD for the first time, you can go back and change these preferences later by going to the Tools->Options menu option, or via the toolbar button.
- Scratch file location: VoltaicHD creates temporary files during conversion, you can set where these should be created to a location of your choice. If you are converting large files from an external storage location, and want to preserve disk space on the machine running the conversions, you should set this location to be on the external storage device.
- Output Directory: You can set where the final converted final files will be placed.
- Extract 5.1ch Audio: The audio track from your movie can be extracted during the conversion process.
- Output Format: WMV format is the recommended format for your converted clips.
Once you’ve got VoltaicHD installed on your system and Preferences all set up you are ready to go. Although it’s worth keeping in mind some suggestions for converting your AVCHD clips:
- Make sure to copy all clips from your camera onto your hard drive before converting. It’s not worth risking trying to convert footage straight from your camera as it can be problematic.
- Keep a VoltaicHD shortcut on your Desktop, this makes it easy to just drag AVCHD clips onto it ready for conversion, or just to open up the application ;)
- Try closing down any unnecessary programs during the conversion process. Converting AVCHD footage is very processor / memory intensive so freeing up resources on your computer helps a lot.
- Watch out when converting large AVCHD files if using a FAT32 formatted drive as the converted files may result in files larger than the 2Gb limitation of FAT32 will allow.
Next, add some AVCHD files to the file list and press Start. The converted files are created in the same directory as the source files by default, or to the location you set in your Preferences.
Setting up and editing in Windows Movie Maker
You need to set up Movie Maker to the correct video format for your region, either PAL or NTSC, and also to widescreen (16:9). Go to Tools->Options and click on the Advanced tab. You should then see a section called Video properties where you can set the correct format (NTSC or PAL) and also the Aspect ratio to 16:9. There’s no need to set the video format (NTSC or PAL) in VoltaicHD as this is auto-detected from the AVCHD clip.
You can now edit your HD footage just like you would with any other footage in Windows Movie Maker.
Exporting from Windows Movie Maker
VoltaicHD provides an export profile for Movie Maker 2.1 on Windows XP which ensures that the full HD resolution of your completed movie can be exported.
To Export from Movie Maker, select the File->Save Movie menu option. This starts the Save Movie Wizard. Use the following settings:
- Movie Location: My Computer
- Choose a name for your exported movie
- Movie Setting: select Other, then VoltaicHD 1080 from the drop down.
- Note: Select VoltaicHD 1080 PAL or NTSC, based on the format you are using.
If you are using Movie Maker in Windows Vista, then VoltaicHD provides an export profile to ensure that the full HD resolution of your completed movie can be exported. If your movies are in 1440×1080 resolution you will also need to manually apply an Effect to your clips to retain the full 16:9 aspect or Widescreen mode. Once your clips are in your storyboard or timeline, right click each of the clips and select “Effect”. On the next window under “Available Effects” scroll down and click on “VoltaicHD Widescreen” then select “Add >>". Then select OK. The preview window should now be showing your clip in widescreen mode.
To Export from Movie Maker, select the File->Publish Movie menu option. This starts the Save Movie Wizard. Use the following settings:
- Movie Location: My Computer
- Choose a name for your exported movie
- Movie Setting: select Other, then VoltaicHD 1080 from the drop down.
- Note: Select VoltaicHD 1080 PAL or NTSC, based on the format you are using.
Movie Maker will then create your HD movie! All thanks to VoltaicHD for PC!
Playing back your HD footage
If you want to watch your HD footage on something other than your PC then you can watch on XBox, PS3 or any Blu-ray player. You’ll need something like Nero to burn a blu-ray DVD (AVCREC format).
The makers of VoltaicHD for PC make some software called RevolverHD which can create blu-ray compatible DVDs. However, there’s currently only a Mac version available, so if you happen to have access to a Mac then you can use that. If you’d like a PC version of RevolverHD then get in touch with the guys at Shedworx and let them know.
Happy editing :)
Update – VoltaicHD 2 released in October 2009
Shedworx have released version 2 of VoltaicHD adding new features such as preview of AVCHD / AVCHD Lite clips, native editing of AVCHD video and the ability to upload video to YouTube. I’ve written a post with an overview of VoltaicHD 2.
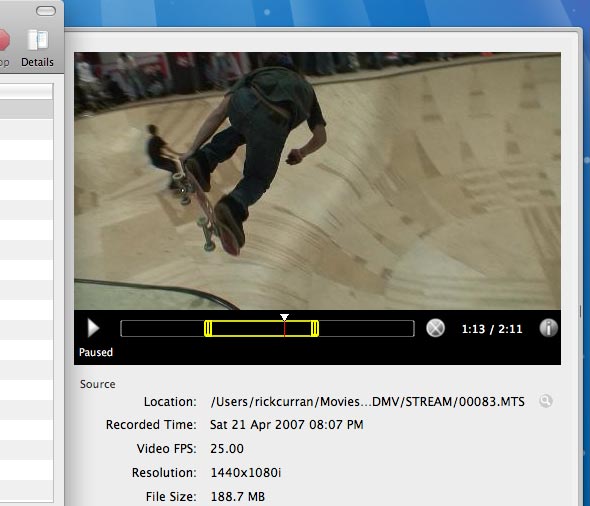
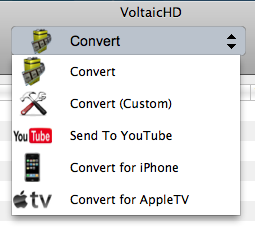 Along with the new preview / edit capability there is also the ability to convert and upload trimmed clips to YouTube directly from VoltaicHD 2.0. There are also preset output options for iPhone / iPod and AppleTV.
Along with the new preview / edit capability there is also the ability to convert and upload trimmed clips to YouTube directly from VoltaicHD 2.0. There are also preset output options for iPhone / iPod and AppleTV.